Difference between revisions of "General Information"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
;21. [[General Information/Transposase expression and activity|Transposase expression and activity]] | ;21. [[General Information/Transposase expression and activity|Transposase expression and activity]] | ||
| − | ;22. [[General Information/ClpX, ClpP, and Lon|ClpX, ClpP, and Lon]] | + | ;22. [[General Information/ClpX, ClpP, and Lon|ATP-dependent proteases (ClpX, ClpP, and Lon)]] |
;23. [[General Information/Reaction mechanisms|Reaction mechanisms]] | ;23. [[General Information/Reaction mechanisms|Reaction mechanisms]] | ||
| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
; | ; | ||
| − | <br/><br/> | + | |
| − | <hr/> | + | <br /><br /> |
| + | <hr /> | ||
Revision as of 13:53, 15 June 2020

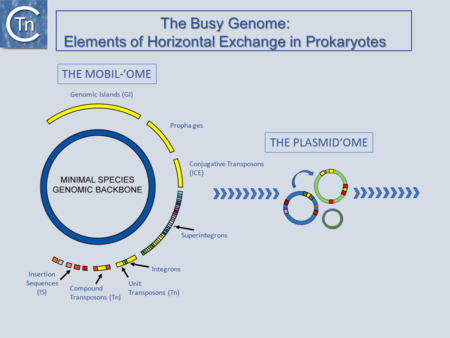
Fig.1.1. The Busy Genome: Elements of Horizontal Exchange. The genome backbone, which includes housekeeping genes, is shown as the inner circle (blue). The "mobilome" is shown in the outer circle. This includes a number of different types of MGE both intercellular (some genomic islands, prophages, and conjugative transposons) and intracellular (Insertion sequences, compound and unit transposons, integrons, and super integrons). An important class of intercellular MGE, the plasmids, act as transposon vectors and facilitate TE movement within the plasmidome.
|