Difference between revisions of "General Information/What Is an IS?"
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
|single ORF||800–1200||0–9||N||1||— | |single ORF||800–1200||0–9||N||1||— | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |IS<i>Mhu11</i>||900–4600||0–10||Y||2||ORFAB | + | |[[IS Families/IS1 family#Major IS1 features|IS<i>Mhu11</i>]]||900–4600||0–10||Y||2||ORFAB |
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan="9" |[[IS Families/IS1595 family|IS<i>1595</i>]] | | rowspan="9" |[[IS Families/IS1595 family|IS<i>1595</i>]] | ||
| − | |IS<i>Pna2</i>||1000–1150||8||GGCnnTG|| rowspan="9" |Y||1|| rowspan="9" |—||DDNK|| rowspan="9" |copy-and-paste (?) | + | |[[IS Families/IS1595 family#ISPna2 group|IS<i>Pna2</i>]]||1000–1150||8||GGCnnTG|| rowspan="9" |Y||1|| rowspan="9" |—||DDNK|| rowspan="9" |copy-and-paste (?) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |IS<i>Pna2</i>+pass||1500–2600||8||— | + | |[[IS Families/IS1595 family#ISPna2 group|IS<i>Pna2</i>+pass]]||1500–2600||8||— |
|1+pass||— | |1+pass||— | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |IS<i>H4</i>||1000||8||CGCTCTT | + | |[[IS Families/IS1595 family#ISH4 archaeal group|IS<i>H4</i>]]||1000||8||CGCTCTT |
| rowspan="5" |1||DDNK | | rowspan="5" |1||DDNK | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |IS<i>1016</i>||700–745||7–9||GGGgctg||DDEK | + | |[[IS Families/IS1595 family#IS1016 group|IS<i>1016</i>]]||700–745||7–9||GGGgctg||DDEK |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |IS<i>1595</i>||900–1100||8||CcTGATT||DDNK+ER4R7 | + | |[[IS Families/IS1595 family#IS1595 group|IS<i>1595</i>]]||900–1100||8||CcTGATT||DDNK+ER4R7 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |IS<i>Sod11</i>||1000–1100||8||nnnGcnTATC||DDHK+ER4R7 | + | |[[IS Families/IS1595 family#ISSod11 group|IS<i>Sod11</i>]]||1000–1100||8||nnnGcnTATC||DDHK+ER4R7 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |IS''Nwi1''||1080–1200||8||ggnnatTAT||DDEK+ER4 | + | |[[IS Families/IS1595 family#ISNwi1 group|IS''Nwi1'']]||1080–1200||8||ggnnatTAT||DDEK+ER4 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |IS<i>Nwi1</i>+pass||1750–4750||8||— | + | |[[IS Families/IS1595 family#ISNwi1 group|IS<i>Nwi1</i>+pass]]||1750–4750||8||— |
|1+pass||— | |1+pass||— | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |IS<i>Nha5</i>||3450–7900||8||CGGnnTT | + | |[[IS Families/IS1595 family#ISNha5 group|IS<i>Nha5</i>]]||3450–7900||8||CGGnnTT |
|1||DDER/K | |1||DDER/K | ||
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan="5" |[[IS Families/IS3 family|IS<i>3</i>]] | | rowspan="5" |[[IS Families/IS3 family|IS<i>3</i>]] | ||
| − | |IS<i>150</i>||1200–1600||3–4||TG|| rowspan="5" |Y|| rowspan="5" |2|| rowspan="5" |ORFAB|| rowspan="5" |DDE|| rowspan="5" |copy-and-paste | + | |[[IS Families/IS3 family#Organization|IS<i>150</i>]]||1200–1600||3–4||TG|| rowspan="5" |Y|| rowspan="5" |2|| rowspan="5" |ORFAB|| rowspan="5" |DDE|| rowspan="5" |copy-and-paste |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |IS<i>407</i>||1100–1400||4||TG | + | |[[IS Families/IS3 family#Organization|IS<i>407</i>]]||1100–1400||4||TG |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |IS<i>51</i>||1000–1400||3–4||TG | + | |[[IS Families/IS3 family#Organization|IS<i>51</i>]]||1000–1400||3–4||TG |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |IS<i>3</i>||1150–1750||3–4||TGa/g | + | |[[IS Families/IS3 family#Organization|IS<i>3</i>]]||1150–1750||3–4||TGa/g |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |IS<i>2</i>||1300–1400||5||TG | + | |[[IS Families/IS3 family#Organization|IS<i>2</i>]]||1300–1400||5||TG |
|- | |- | ||
|[[IS Families/IS481 family|IS<i>481</i>]] | |[[IS Families/IS481 family|IS<i>481</i>]] | ||
| Line 68: | Line 68: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan="7" |[[IS Families/IS4 and related families|IS<i>4</i>]] | | rowspan="7" |[[IS Families/IS4 and related families|IS<i>4</i>]] | ||
| − | |IS<i>10</i>||1200–1350||9||CT|| rowspan="7" |Y|| rowspan="6" |1|| rowspan="7" |DDE||hairpin intermediate|| rowspan="7" |cut-and-paste | + | |[[IS Families/IS4 and related families#IS10 and IS50|IS<i>10</i>]]||1200–1350||9||CT|| rowspan="7" |Y|| rowspan="6" |1|| rowspan="7" |DDE||hairpin intermediate|| rowspan="7" |cut-and-paste |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |IS<i>50</i>||1350–1550||8–9||C||hairpin intermediate | + | |[[IS Families/IS4 and related families#IS10 and IS50|IS<i>50</i>]]||1350–1550||8–9||C||hairpin intermediate |
|- | |- | ||
|IS<i>Pepr1</i>||1500–1600||7–8||-T-AA||? | |IS<i>Pepr1</i>||1500–1600||7–8||-T-AA||? | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |IS<i>4</i>||1400–1600||10–13||-AAT||? | + | |[[IS Families/IS4 and related families#IS4 family|IS<i>4</i>]]||1400–1600||10–13||-AAT||? |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |IS<i>4Sa</i>||1150–1750||8–10||CA||? | + | |[[IS Families/IS4 and related families#General|IS<i>4Sa</i>]]||1150–1750||8–10||CA||? |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |IS<i>H8</i>||1400–1800||10|| CAT |? | + | |[[IS Families/IS4 and related families#General|IS<i>H8</i>]]||1400–1800||10|| CAT |? |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |IS<i>231</i>||1450–5400||10–12||CAT||1 or + *||*passenger genes | + | |[[IS Families/IS4 and related families#IS231|IS<i>231</i>]]||1450–5400||10–12||CAT||1 or + *||*passenger genes |
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan="2" |[[IS Families/IS4 and related families#IS701 family|IS<i>701</i>]] | | rowspan="2" |[[IS Families/IS4 and related families#IS701 family|IS<i>701</i>]] | ||
| Line 92: | Line 92: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan="6" |[[IS Families/IS5 and related IS1182 families|IS<i>5</i>]] | | rowspan="6" |[[IS Families/IS5 and related IS1182 families|IS<i>5</i>]] | ||
| − | |IS<i>903</i>||950–1150||9||GG|| rowspan="6" |Y|| rowspan="5" |1|| rowspan="5" |—|| rowspan="6" |DDE|| rowspan="6" |— | + | |[[IS Families/IS5 and related IS1182 families#Distribution|IS<i>903</i>]]||950–1150||9||GG|| rowspan="6" |Y|| rowspan="5" |1|| rowspan="5" |—|| rowspan="6" |DDE|| rowspan="6" |— |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |IS<i>L2</i>||850–1200||2–3||— | + | |[[IS Families/IS5 and related IS1182 families#Distribution|IS<i>L2</i>]]||850–1200||2–3||— |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |IS<i>H1</i>||900–1150||8||-GC | + | |[[IS Families/IS5 and related IS1182 families#Distribution|IS<i>H1</i>]]||900–1150||8||-GC |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |IS''5''||1000–1500||4||Ga/g | + | |[[IS Families/IS5 and related IS1182 families#Distribution|IS''5'']]||1000–1500||4||Ga/g |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |IS''1031''||850–1050||3||GAa/g | + | |[[IS Families/IS5 and related IS1182 families#Distribution|IS''1031'']]||850–1050||3||GAa/g |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |IS''427''||800–1000||2–4||Ga/g||2||ORFAB | + | |[[IS Families/IS5 and related IS1182 families#Distribution|IS''427'']]||800–1000||2–4||Ga/g||2||ORFAB |
|- | |- | ||
|[[IS Families/IS5 and related IS1182 families#IS1182|IS<i>1182</i>]]||—||1330–1950||0–60||—||Y||1||—||DDE||— | |[[IS Families/IS5 and related IS1182 families#IS1182|IS<i>1182</i>]]||—||1330–1950||0–60||—||Y||1||—||DDE||— | ||
| Line 120: | Line 120: | ||
|—||1200–1500||8–9||Ga/g|| rowspan="3" |Y|| rowspan="3" |1|| rowspan="3" |—|| rowspan="3" |DDE|| rowspan="3" |copy-and-paste | |—||1200–1500||8–9||Ga/g|| rowspan="3" |Y|| rowspan="3" |1|| rowspan="3" |—|| rowspan="3" |DDE|| rowspan="3" |copy-and-paste | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |IS<i>1249</i>||1300||0–10||GG | + | |[[IS Families/IS256 family#IS1249 group|IS<i>1249</i>]]||1300||0–10||GG |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |IS<i>C1250</i>||1250||0–9||GG | + | |[[IS Families/IS256 family#ISC1250 group|IS<i>C1250</i>]]||1250||0–9||GG |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |IS<i>H6</i>||—||1450||8||GGT||Y||1||—||DDE||— | + | |[[IS Families/IS256 family#ISH6|IS<i>H6</i>]]||—||1450||8||GGT||Y||1||—||DDE||— |
|- | |- | ||
|[[IS Families/IS256 family#ISLre2|IS<i>Lre2</i>]]||—||1500–2000||9||—||Y||1||—||DDE||— | |[[IS Families/IS256 family#ISLre2|IS<i>Lre2</i>]]||—||1500–2000||9||—||Y||1||—||DDE||— | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | rowspan="3" |IS<i>Kra4</i> | + | | rowspan="3" |[[IS Families/IS256 family#ISKra4|IS<i>Kra4</i>]] |
| − | |IS<i>Azba1</i>||1400–2900||0||—|| rowspan="3" |Y||1 or + *||—|| rowspan="3" |DDE|| rowspan="3" |— | + | |[[IS Families/IS256 family#ISAzba1|IS<i>Azba1</i>]]||1400–2900||0||—|| rowspan="3" |Y||1 or + *||—|| rowspan="3" |DDE|| rowspan="3" |— |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |IS<i>Mich2</i>||1250–1400||8||GGG||1 or 2||ORFAB | + | |[[IS Families/IS256 family#ISMich2|IS<i>Mich2</i>]]||1250–1400||8||GGG||1 or 2||ORFAB |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |IS<i>Kra4</i>||1400–3700||9||GGG||1 or + *||— | + | |[[IS Families/IS256 family#ISKra4 2|IS<i>Kra4</i>]]||1400–3700||9||GGG||1 or + *||— |
|- | |- | ||
|[[IS Families/IS630 family|IS<i>630</i>]]||—||1000–1400||2*||—||Y||1 or 2||ORFAB||DDE||cut-and-paste | |[[IS Families/IS630 family|IS<i>630</i>]]||—||1000–1400||2*||—||Y||1 or 2||ORFAB||DDE||cut-and-paste | ||
| Line 154: | Line 154: | ||
|IS<i>1111</i>||—||—||—||Y*||—||—||—||— | |IS<i>1111</i>||—||—||—||Y*||—||—||—||— | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |IS<i>91</i>||—||1500–2000||0||—||N||1||—||HUH/Y2||rolling circle | + | |IS<i>91</i>||—||1500–2000||0||—||N||1||—||HUH/Y2||rolling-circle |
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan="2" |[[IS Families/IS200-IS605 family|IS<i>200/</i>IS<i>605</i>]] | | rowspan="2" |[[IS Families/IS200-IS605 family|IS<i>200/</i>IS<i>605</i>]] | ||
| Line 178: | Line 178: | ||
|I<i>SM1</i>||1300–1600||8–9||—||Y||1 | |I<i>SM1</i>||1300–1600||8–9||—||Y||1 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |IS<i>1202</i> | + | |[[IS Families/IS481 family|IS<i>1202</i>]] |
|1400–1700 | |1400–1700 | ||
|5 | |5 | ||
Revision as of 14:10, 4 June 2020
Contents
Classical IS
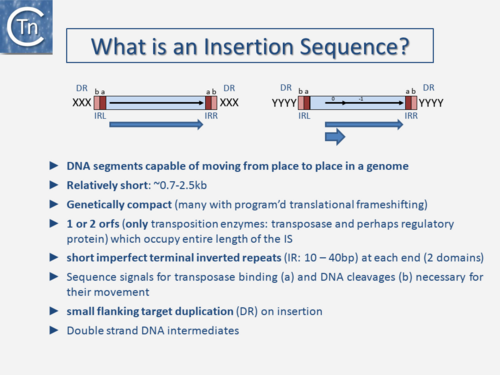
The original definition of an IS (Fig.3.1) was: a short, generally phenotypically cryptic, DNA segment encoding only the enzymes necessary for its transposition and capable of repeated insertion into many different sites within a genome using mechanisms independent of large regions of DNA homology between the IS and target [1]. Classical IS are between 0.7 and 2.5 kb in length, genetically compact with one or two open reading frames (orfs) which occupy the entire length of the IS and terminate in flanking imperfect terminal repeat sequences (IR) (Table 1). The orfs include the Tpase that catalyzes the DNA cleavages and strand transfers leading to IS movement and, in some cases, regulatory proteins. Their highly compact nature is illustrated by the fact that some IS have developed “recoding” strategies such as Programmed Ribosomal Frameshifting (involving ribosome slippage) and Programmed Transcriptional Realignment (involving RNA polymerase slippage) [2][3][4][5][6][7][8].
These permit assembly of different functional protein domains effectively encoding two proteins of different functions in one DNA segment. IS also often generates a short flanking directly repeated duplication (DR) of the target DNA on insertion. These characteristics are not limited to prokaryotic IS but are also shared with most eukaryotic DNA transposons. Classical IS generally transpose using a double-strand DNA intermediate. However, for prokaryotic IS, this strict definition has been broadened over the years with the discovery of an increasing number of non-canonical derivatives and variants, some of which are described in the following sections. Moreover, as we learn more about diversity from sequenced genomes, classification is becoming more problematic because the large degree of MGE diversity is obscuring the borders between certain types of TE (see "Fuzzy Borders") [9]. Despite their abundance and diversity, the number of different chemical mechanisms used in TE movement is surprisingly limited and many quite divergent TE share a similar mechanism.
Characteristics of insertion sequence families
| Table 1. Abbreviations: DR, duplication repeat; IS, insertion sequence; ORF, open reading frame. | |||||||||
| Families | Sub-Groups | Typical size-range (bp) | DR (bp) | Ends | IRs | No ORFs | Frameshift | Catalytic residues | Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IS1 | — | 740–1180 | 8–9 | GGnnnTG | Y | 2 | ORFAB | DDE | copy-and-paste and cointegrate |
| single ORF | 800–1200 | 0–9 | N | 1 | — | ||||
| ISMhu11 | 900–4600 | 0–10 | Y | 2 | ORFAB | ||||
| IS1595 | ISPna2 | 1000–1150 | 8 | GGCnnTG | Y | 1 | — | DDNK | copy-and-paste (?) |
| ISPna2+pass | 1500–2600 | 8 | — | 1+pass | — | ||||
| ISH4 | 1000 | 8 | CGCTCTT | 1 | DDNK | ||||
| IS1016 | 700–745 | 7–9 | GGGgctg | DDEK | |||||
| IS1595 | 900–1100 | 8 | CcTGATT | DDNK+ER4R7 | |||||
| ISSod11 | 1000–1100 | 8 | nnnGcnTATC | DDHK+ER4R7 | |||||
| ISNwi1 | 1080–1200 | 8 | ggnnatTAT | DDEK+ER4 | |||||
| ISNwi1+pass | 1750–4750 | 8 | — | 1+pass | — | ||||
| ISNha5 | 3450–7900 | 8 | CGGnnTT | 1 | DDER/K | ||||
| IS3 | IS150 | 1200–1600 | 3–4 | TG | Y | 2 | ORFAB | DDE | copy-and-paste |
| IS407 | 1100–1400 | 4 | TG | ||||||
| IS51 | 1000–1400 | 3–4 | TG | ||||||
| IS3 | 1150–1750 | 3–4 | TGa/g | ||||||
| IS2 | 1300–1400 | 5 | TG | ||||||
| IS481 | — | 950–1300 | 4–15 | TGT | Y | 1 | — | DDE | copy-and-paste (?) |
| IS4 | IS10 | 1200–1350 | 9 | CT | Y | 1 | DDE | hairpin intermediate | cut-and-paste |
| IS50 | 1350–1550 | 8–9 | C | hairpin intermediate | |||||
| ISPepr1 | 1500–1600 | 7–8 | -T-AA | ? | |||||
| IS4 | 1400–1600 | 10–13 | -AAT | ? | |||||
| IS4Sa | 1150–1750 | 8–10 | CA | ? | |||||
| ISH8 | 1400–1800 | 10 | ? | ||||||
| IS231 | 1450–5400 | 10–12 | CAT | 1 or + * | *passenger genes | ||||
| IS701 | — | 1400–1550 | 4 | — | Y | 1 | — | DDE | — |
| ISAba11 | — | — | |||||||
| ISH3 | — | 1225–1500 | 4–5 | C-GT | Y | 1 | — | DDE | — |
| IS1634 | — | 1500–2000 | 5–6 | C | Y | 1 | — | DDE | — |
| IS5 | IS903 | 950–1150 | 9 | GG | Y | 1 | — | DDE | — |
| ISL2 | 850–1200 | 2–3 | — | ||||||
| ISH1 | 900–1150 | 8 | -GC | ||||||
| IS5 | 1000–1500 | 4 | Ga/g | ||||||
| IS1031 | 850–1050 | 3 | GAa/g | ||||||
| IS427 | 800–1000 | 2–4 | Ga/g | 2 | ORFAB | ||||
| IS1182 | — | 1330–1950 | 0–60 | — | Y | 1 | — | DDE | — |
| IS6 | — | 700–900 | 8 | GG | Y | 1 | — | DDE | co-integrate |
| IS21 | — | 1750–2600 | 4–8 | TG | Y | 2 * | — | DDE | — |
| IS30 | — | 1000–1700 | 2–3 | — | Y | 1 | — | DDE | copy-and-paste |
| IS66 | — | 2000–3000 | 8–9 | GTAA | Y | 3* | — | DDE* | — |
| ISBst12 | 1350–1900 | 1 | DDE | ||||||
| IS256 | — | 1200–1500 | 8–9 | Ga/g | Y | 1 | — | DDE | copy-and-paste |
| IS1249 | 1300 | 0–10 | GG | ||||||
| ISC1250 | 1250 | 0–9 | GG | ||||||
| ISH6 | — | 1450 | 8 | GGT | Y | 1 | — | DDE | — |
| ISLre2 | — | 1500–2000 | 9 | — | Y | 1 | — | DDE | — |
| ISKra4 | ISAzba1 | 1400–2900 | 0 | — | Y | 1 or + * | — | DDE | — |
| ISMich2 | 1250–1400 | 8 | GGG | 1 or 2 | ORFAB | ||||
| ISKra4 | 1400–3700 | 9 | GGG | 1 or + * | — | ||||
| IS630 | — | 1000–1400 | 2* | — | Y | 1 or 2 | ORFAB | DDE | cut-and-paste |
| IS982 | — | 1000 | 3–9 | AC | Y | 1 | — | DDE | — |
| IS1380 | — | 1550–2000 | 4–5 | CC | Y | 1 | — | DDE | — |
| ISAs1 | — | 1200–1500 | 8–10 | CAGGG | Y | 1 | — | — | — |
| ISL3 | — | 1300–2300 | 8 | GG | Y | 1 | — | — | — |
| Tn3 | — | >3000 | 0 | GGGG | Y | >1 | — | DDE | co-integrate |
| ISAzo13 | — | 1250–2200 | 0–4 | Ga/g | Y | 1 | — | — | — |
| IS110 | — | 1200–1550 | 0 | — | N | 1 | — | DEDD | — |
| IS1111 | — | — | — | Y* | — | — | — | — | |
| IS91 | — | 1500–2000 | 0 | — | N | 1 | — | HUH/Y2 | rolling-circle |
| IS200/IS605 | IS200 | 600–750 | 0 | — | 0 | 1* | — | HUH/Y1 | peel-and-paste |
| IS605 | 1300–2000 | — | — | — | 2* | — | HUH/Y1** | ||
| IS607 | — | 1700–2500 | 0 | — | N | 2* | — | Serine** | — |
| ISNCY | IS892 | 1600 | 0–8 | CTAG | Y | 2 | ORFAB | — | — |
| ISLbi1 | 1400–1500 | 5 | — | Y | 1 | ||||
| ISMae2 | 1400–2400 | 9 | CAG | Y | 1 | ||||
| ISPlu15 | 800–1000 | 0 | — | N | 1 | ||||
| ISA1214 | 1000–1200 | 8–12 | — | Y | 2 | ||||
| ISC1217 | 1200 | 6–8 | TAG | Y | 1 | ||||
| ISM1 | 1300–1600 | 8–9 | — | Y | 1 | ||||
| IS1202 | 1400–1700 | 5 | TGT | Y | 1 | — | DDEQ | — | |
| ISDol1 | 1600–1900 | 6–7 | — | Y | 1 | — | DDE | — | |
New types of IS
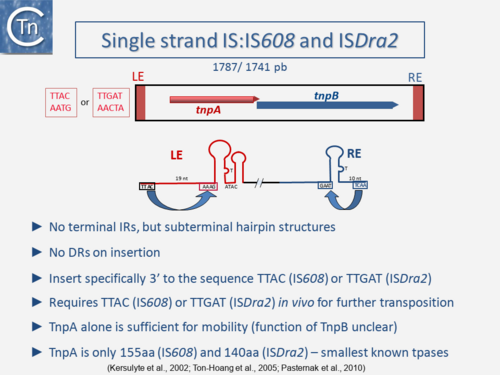
One example of this expanding diversity is the identification of another entire class of IS [10][11][12]. Members of this class use an entirely different mechanism of transposition involving single-strand circular DNA intermediates which appear to target stalled replication forks [13] (Fig.3.2). They possess small transposases (~150 aa) which are completely different to the classical IS in the type of chemistry they catalyze (Groups with HUH Enzymes). Another example are the casposons which are related to CRISPRs but whose transposition has yet to be fully characterized [14][15][16][17].
Bibliography
- ↑ <pubmed>26104715</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed> 21673094</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>24499397</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>26350305</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed> 21478364</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>11125107</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>8384687</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>12762024</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>24499397</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>10986230</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>9858724</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>11807059</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>26350330</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>24884953</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>28472712</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>28683354</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>26104718</pubmed>