Difference between revisions of "General Information/ IS derivatives of Tn3 family transposons"
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
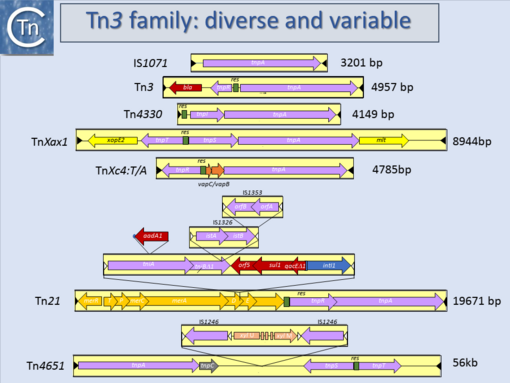
|[[Image:1.15.1.png|thumb|center|510x510px|'''Fig. 1.15.1.''' Tn''3'' family characteristics. | |[[Image:1.15.1.png|thumb|center|510x510px|'''Fig. 1.15.1.''' Tn''3'' family characteristics. | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| − | + | .|alt=|border]] | |
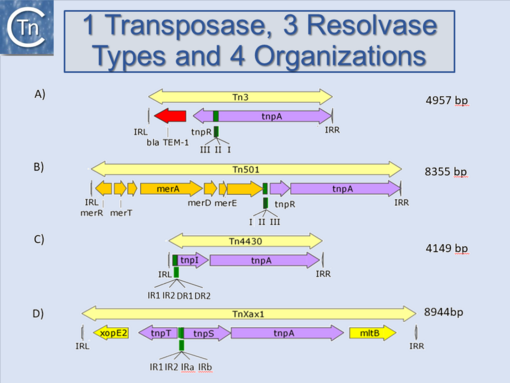
|[[Image:1.15.2.png|thumb|center|510x510px|'''Fig. 1.15.2.''' Tn''3'' family resolvase configuration. | |[[Image:1.15.2.png|thumb|center|510x510px|'''Fig. 1.15.2.''' Tn''3'' family resolvase configuration. | ||
Revision as of 23:15, 4 May 2020
Another source of ambiguity for classification purposes occurs in the Tn3 family (see section “Tn families”) (Fig.1.15.1 and 1.15.2). Tn3 family members are quite variable. They include a number of diverse passenger genes that can represent entire operons, notably mercury resistance, or individual genes involved in antibiotic resistance, breakdown of halogenated aromatics, or virulence [e.g. [1]]]. They often carry integron recombination platforms enabling them to incorporate additional resistance genes by recruiting integron cassettes[2]. Members are quite characteristic: they have long relatively well conserved IR and a particularly long Tpase (950 to 1025 aa). They also encode a site-specific recombination (“resolution”) system necessary for completion of their transposition[3]. There are a number of different resolution systems associated with different members of this family (Fig.1.15.2) IS1071, (Fig.1.15.1) composed of Tn3-like IR and Tpase gene but lacking both the site-specific recombination system and passenger genes was identified many years ago[4][5]. This clearly accords with the definition of an IS. Several other examples have now been identified (e.g. ISVsa19, ISShfr9, ISBusp1).