General Information/The casposases
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
The casposases
More recently, TE related to CRISPRs, Casposons have been identified[1] and a reassement of their ends has led to the identification of an 14-15 bp target duplication. Moreover, the purified Cas1 enzyme encoded by these ancestral transposons has been demonstrated to catalyse strand transfer of a pre-cleaved transposon in vitro but does not appear to promote transposon strand cleavage in this assay[2]. Cas1 "casposases" use similar chemistry to that used by the CRISPR Cas1-Cas2 complex but with opposite substrate specificities since CRISPR Cas1-Cas2 integrates "random" sequences into a specific site in the CRISPR locus whereas casposases integrate specific site (the casposon ends) into random target sequences.

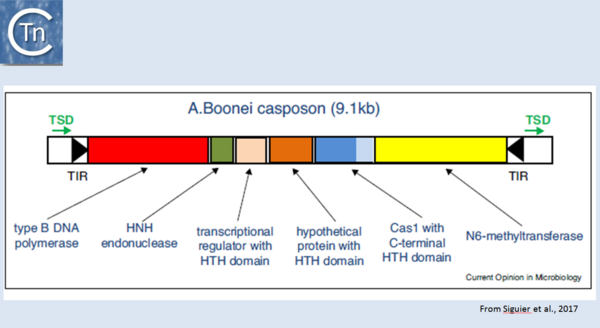
Fig 1.44. Organization of the A. boonei casposon. The casposon is shown as an unfilled box. Black filled arrow-heads represent the terminal inverted repeats (TIR); green arrows, the target site duplication (TSD); the genes areas follows: type B DNA polymerase (red box); HNH endonuclease (green); transcriptional regulator with HTH domain (pink); hypothetical protein with HTH domain (orange); cas1 (dark blue) with a c-terminal HTH (light blue); N6-methyltransferase (yellow). From Hickman and Dyda (2015). Non-CRISPR-associated cas1 form two distinct clades. One contains three distinct casposon families (1, 2 and 3) which share features with eukaryotic Polinton/Maverick eukaryotic transposons labelled ‘self-synthesizing’ since they include B family DNA polymerase genes. Members of the three families differ in gene content and evolutionary provenance of the DNA polymerases (protein-primed or RNA-primed).
Bibliography