Glossary
A
B
C
- Class I Elements: (see also)
- Class II Elements: (see also)
- Cre Recombinase: The Cre Recombinase is a DNA breaking and rejoining enzyme (from tyrosine recombinase family) derived from the P1 bacteriophage. It is widely used for conditional mutagenesis of transgenes and insert DNA cassettes into eukaryotic chromosomes. (see also).
- Co-integrate:
- Copy-and-paste transposition model:
- Copy-out–Paste-in transposition model:
- Cut-and-paste transposition model:
D
- Direct Repeats (DRs):
- DDE Domain:
- Donor Primed Replicative Transposition (DPRT):
E
F
G
- Group II introns: The group II introns are mobile retroelements that use the combined activities of an autocatalytic RNA and an intron-encoded reverse transcriptase (RT) to propagate efficiently within genomes. They are intimately related with the evolution of eukaryotes, being ancestrally related to nuclear spliceosomal introns, retrotransposons and telomerase (see also).
- Genome decay:
- Genome Rearrangements:
H
- Horizontal gene transfer (or Lateral gene transfer):
- Homologous recombination:
I
- Inverted Repeats (IR):
- Integron: Integrons one class of Mobile Genetic Elements (MGEs) are specific genetic structure composed by genes (named as integron cassettes) that generally allow bacteria to adapt and rapidly evolve through the acquisition, stockpiling, excision, and reordering of open reading frames found the integron cassettes. The integron mobilization is mediated by site-specific recombination reactions by the integrase (see also).
- Invertases:
J
K
L
M
- Mobilome:
- Methylase (Methylation):
N
O
P
- Plasmidome:
- Pseudogenisation:
- Peel-and-paste (Single-strand) transposition model:
- Phage tyrosine integrase:
- Phage serine integrase:
Q
R
- Resolution site:
- Resolvase:
- Rolling-circle transposition model:
S
- Synaptic complex:
- Serine recombinase: The serine recombinases are a family of DNA breaking and rejoining enzymes. Unlike homologous recombination, the serine recombinases promote rearrangements of DNA by breaking and rejoining strands at precisely defined sequence positions (see also).
- Serine Resolvases: The serine resolvases and the closely related invertases, are a group of site-specific recombinases that, in their native contexts, resolve large fused replicons into smaller separated ones
- Single-strand transposition:
- Site-specific recombination:
T
- Target specificity:
- Transposase:
- Transposome:
- Target Primed Replicative Transposition (TPRT):
- Tyrosine recombinase: Tyrosine site-specific recombinases (YRs) are a family of DNA breaking and rejoining enzymes which use the active site tyrosine nucleophile for DNA strand breakage (see also).
U
V
- V(D)J Recombination:
W
X
- Xer Site-Specific Recombination:
Y
Z
See also
The logic behind the IS nomenclature and naming attribution
The first attempt to create an concise nomenclature system for Transposable Elements started at Stanford University by Campbell and colleagues in 1979 [1]. They classified the prokaryotes elements as simple IS elements to more complex Tn transposons, and self-replicating episomes. In addition, definitions and nomenclature rules for these three classes of prokaryotic TEs were specified [1].
Page Template:Quote/styles.css has no content.
Transposable elements are specific DNA segments that can repeatedly insert into a few or many sites in a genome
—Campbell et al 1979
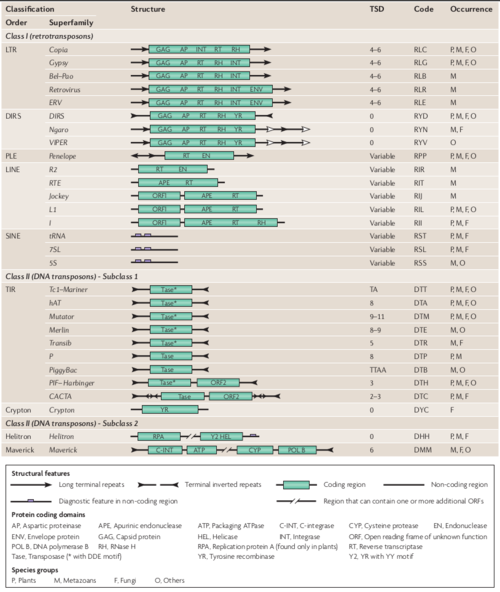
Proposed classification system for eukaryotic Transposable Elements (TEs) (extracted from Wicker et al., 2007).