Difference between revisions of "IS Families/IS1 family"
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
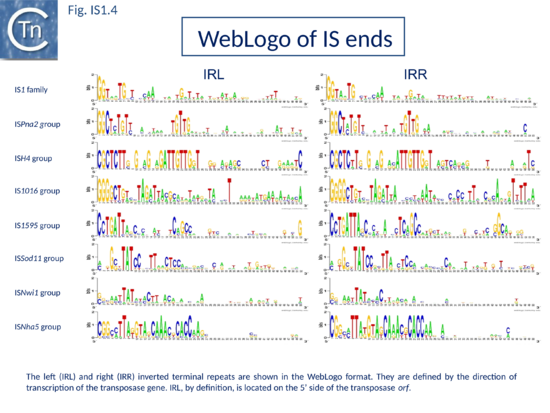
[[Image:Fig.IS1.4.png|thumb|center|550x550px|'''Fig.IS1.4.''' Weblogo results showing the commons IS''1'' ends.|alt=]] | [[Image:Fig.IS1.4.png|thumb|center|550x550px|'''Fig.IS1.4.''' Weblogo results showing the commons IS''1'' ends.|alt=]] | ||
| − | + | ====Major IS features==== | |
{| class="wikitable" style="margin:auto" | {| class="wikitable" style="margin:auto" | ||
| colspan="9" |'''Table 1.''' Major IS features. The table summarises from left to right: the IS family; groups defined in the MCL analysis; the number of members identified in each group; the length ranges for each group; the length of the flanking direct repeats (DR); the consensus sequence of the terminal inverted repeats (IRs); length range of the transposase; the presence of Zinc Finger (Zn) and helix turn helix (HTH) motifs (HTH prediction used PBIL (http://pbil.univ-lyon1.fr); * indicates that the prediction was weak); the potential catalytic site residues; and whether the transposase gene intrudes on the right IS end. | | colspan="9" |'''Table 1.''' Major IS features. The table summarises from left to right: the IS family; groups defined in the MCL analysis; the number of members identified in each group; the length ranges for each group; the length of the flanking direct repeats (DR); the consensus sequence of the terminal inverted repeats (IRs); length range of the transposase; the presence of Zinc Finger (Zn) and helix turn helix (HTH) motifs (HTH prediction used PBIL (http://pbil.univ-lyon1.fr); * indicates that the prediction was weak); the potential catalytic site residues; and whether the transposase gene intrudes on the right IS end. | ||
Revision as of 18:21, 21 May 2020
Contents
- 1 General
- 2 Presence in compound transposons
- 3 Presence in plasmids: the resistance determinant (r-det)
- 4 Distribution
- 5 Organization
- 6 IS1 sub-groups and transposase organization
- 7 Non-canonical IS1 derivatives in bacteria and archaea
- 8 Canonical archaeal IS1 derivatives
- 9 Target specificity
- 10 Transposase expression by programmed translational frameshifting
- 11 Transcription termination?
- 12 Mechanism
General
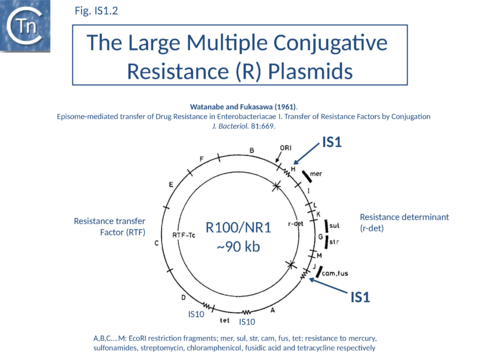
As its name suggests, IS1 was one of the earliest IS to be identified[1][2] and it is one of the shortest (Fig. IS1.1). The original examples were obtained from an F'lac-proB plasmid (IS1K[3]) and the multiple drug resistance plasmid R100 (IS1R[4] (Fig. IS1.2). The nucleotide sequences of several variants of this IS from Escherichia and Shigella species were determined e.g. [5]. Of the 17 initially compared, three were duplicates and one only partially complete. Nine of the others exhibited sequence divergence of between 0.52 and 10% at the nucleic acid level. These were called IS1 isoforms. Two examples, IS1N and IS1H, were significantly different from the others (45 to 47% divergence in nucleotide sequence; 55 to 58% divergence at the protein level) but similar to each other (14 to 19% divergence at the protein level) and might be considered distinct members of the family. Except for IS1K(A) and IS1R(G), transposition of these elements was not directly demonstrated experimentally in a controlled way but is implied from the isolation of mutants with spontaneous mutations in various genes.
Presence in compound transposons
IS1 is a component of several compound transposons such as Tn9[6] (Fig.1.2.3) and Tn1681[7][8] where it is present in direct or inverted orientation flanking a chloramphenicol acetyltransferase and heat-stable toxin gene, respectively. Tn9 was initially isolated on bacteriophage P1 following infection with of a strain of Escherichia coli carrying the antibiotic resistance (R) plasmid Rms 14[9][10]. Measurement of the transposition frequency of a set of IS1-derived compound transposons located in the same genetic environment showed that the frequency of transposition decreased by a factor of 2 for each kilobase of DNA included between two directly repeated IS1 copies[11].
Presence in plasmids: the resistance determinant (r-det)
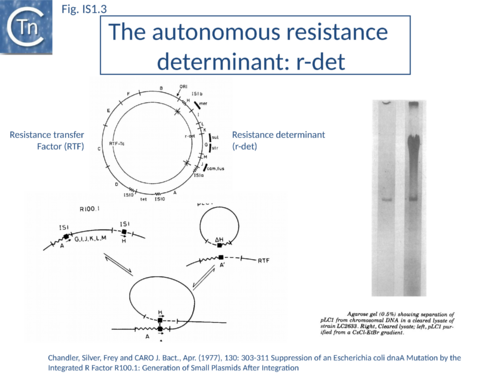
IS1 is also found in several conjugative plasmids flanking large regions carrying a number of antibiotic resistance genes (resistance determinant or r-det) (see [12]]) (Fig. IS1.2) and can participate in homologous recombination to generate circular r-det forms or tandem multimers resulting in increased antibiotic resistance[13]. R-det structures are associated with autonomously replicating, self-transmissible plasmid units, the resistance transfer factor (RTF). In plasmids of the R100 or NR1 family the r-det can demonstrate a measure of autonomy from the RTF: in Proteus mirabilis it is amplified (increasing its number of copies) relative to the RTF when the host cell is grown in the presence of chloramphenicol[14][15]; in Salmonella typhimurium it is excised and lost, at high frequency, from the parent R100.1 plasmid, in a process which depends on the host recombination system[16]. In E. coli 1 to 2 r-det molecules per cell appear in a closed circular form in certain E. coli strains in which R100.1 has been integrated in the chromosome[17] (Fig. IS1.3). Their appearance also depends on the host recombination system[18][19][20]. The results of experiments in which the r-det of NR1 or R100 was transposed to bacteriophage P1[21][22] suggested that Tn9 was originally derived by IS1-mediated deletion from a structure similar to an r-det.
Distribution
Although IS1 was originally thought to be restricted to the enterobacteria[23][24][25](Escherichia, Shigella, Yersinia, Klebsiella, Pantoea, Edwardsiella), it has now been identified in other bacterial genera including cyanobacteria (Synechocystis[26][27] Acaryochloris marina, Nostoc and Arthrospira), archaea (Sulfolobus and Methanosarcina), Deinococcus, and Pseudomonas.
Organization
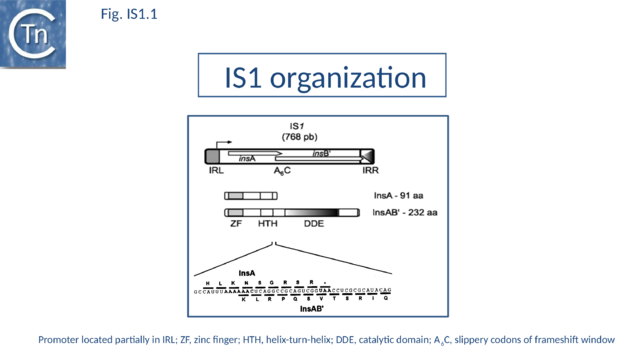
The founding IS1 family member is 768 bp long (Fig. IS1.1) and is bordered by 23-bp imperfect Inverted Repeats (IRL and IRR). Other members are also short (700-800 bp), bordered by relatively well conserved 15-24 bp inverted repeats (Fig. IS1.4; Table 1) and generate a 9 bp target Direct Repeats (DR) [28][29] or more rarely DR of 8, 10, and 14 bp on integration[30][31][32]. The frequency of appearance of DR of non-canonical length was reported to be increased by mutations within the Tpase gene although no further information is available[33].
Major IS features
| Table 1. Major IS features. The table summarises from left to right: the IS family; groups defined in the MCL analysis; the number of members identified in each group; the length ranges for each group; the length of the flanking direct repeats (DR); the consensus sequence of the terminal inverted repeats (IRs); length range of the transposase; the presence of Zinc Finger (Zn) and helix turn helix (HTH) motifs (HTH prediction used PBIL (http://pbil.univ-lyon1.fr); * indicates that the prediction was weak); the potential catalytic site residues; and whether the transposase gene intrudes on the right IS end. | ||||||||
| Groups | No. | Length (bp) | DR (bp) | IR consensus | Tnp (aa) | Tnp Motif | Catalytic motif | Tnp in IRR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IS1 family | ||||||||
| IS1 (classic) | 22 | 700-800 | 8-9 | GGnnnT –G–––– |
220-245 | Zn, HTH | DDER | Y |
| IS1 (with 1 ORF) | 8 | 800-1200 | 0-9 | GGnnnT –G–––– |
230-320 | Zn, HTH | DDER | Y |
| ISMhu11 | 13 | 900-4600 | 0-10 | GGnnnT –G–––– |
HTH | DDER | Y | |
| IS1595 family | ||||||||
| ISPna2 (classic) | 11 | 1000-1150 | 8 | GGCnnT –G–––– |
320-345 | Zn, HTH | D(D)DNK | Y |
| ISPna2 (with extra DNA) | 1 | 1635 | 8 | GGCnnT –G–––– |
347 | Zn, HTH | D(D)DNK | N |
| ISPna2 (with passengers) | 6 | 1500-2600 | 8 | GGCnnT –G–––– |
340-355 | Zn, HTH | D(D)DNK | N |
| ISH4 | 4 | 1000 | 8 | CGCTCT –T–––– |
270-295 | Zn, HTH | D(D)DER | Y |
| IS1016 | 19 | 700-745 | 7-9 | GGGgct –g–––– |
200-230 | HTH | DDEK + E4R | Y/N |
| IS1595 | 16 | 900-1100 | 8 | CcTGAT –T–––– |
270-330 | Zn, HTH* | DDNK + E4R7R | Y |
| ISSod11 | 16 | 1000-1100 | nnnGcnTA –––T–––– |
300-345 | Zn, HTH* | DDHK + E4R7R | Y/N | |
| ISNwi1 (classic) | 2 | 1080-1200 | 8 | ggnnatTAT | 330-365 | Zn, HTH | DDEK + E4R | N |
| ISNwi1 (with extra DNA) | 3 | 1860-2350 | 8 | ggnnatTAT | 300-355 | Zn, HTH | DDEK + E4R | N |
| ISNwi1 (with passengers) | 13 | 1750-4750 | 8 | ggnnatTAT | 280-330 | Zn, HTH | DDEK + E4R | N |
| ISNha5 | 11 | 3450-7900 | 8 | CGGnnT –T–––– |
320-385 | Zn, HTH* | DDER/K | N |
| Total | 145 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
IS1 carries partly overlapping open reading frames (insA and insB’) located in the 0 and -1 relative translational phases[34][35] and expressed from a promoter, pIRL, partially located in IRL[36] (Fig. IS1.1) and the transposase, InsAB’, is produced by programmed -1 translational frameshifting (see below). However, some IS1-family members have now been identified in which InsAB’ is expressed from a single open reading frame (see below). Each of the IR of the original IS1 carry a functional binding site for the DNA architectural protein, IHF (integration host factor). However, a role for IHF in either transposase expression or IS1 transposition remains unknown[37][38]. The IRs were divided into two functional domains: an internal domain necessary for sequence-specific binding of IS1 transposition proteins and a short “tip” which is necessary for cleavage and strand transfer[39] (Fig. 1.26.1). Transcription through these IR appears to inhibit transposition activity presumably by disrupting the formation of the IS1 transpososome[40][41][42].
IS1 sub-groups and transposase organization
The predicted secondary structure features of the active site of the IS1 transposase catalytic core are in excellent agreement with those obtained from the structure of the HIV IN core (Fig. IS1.5A) confirming the relationship with other members of the DDE class of transposases.
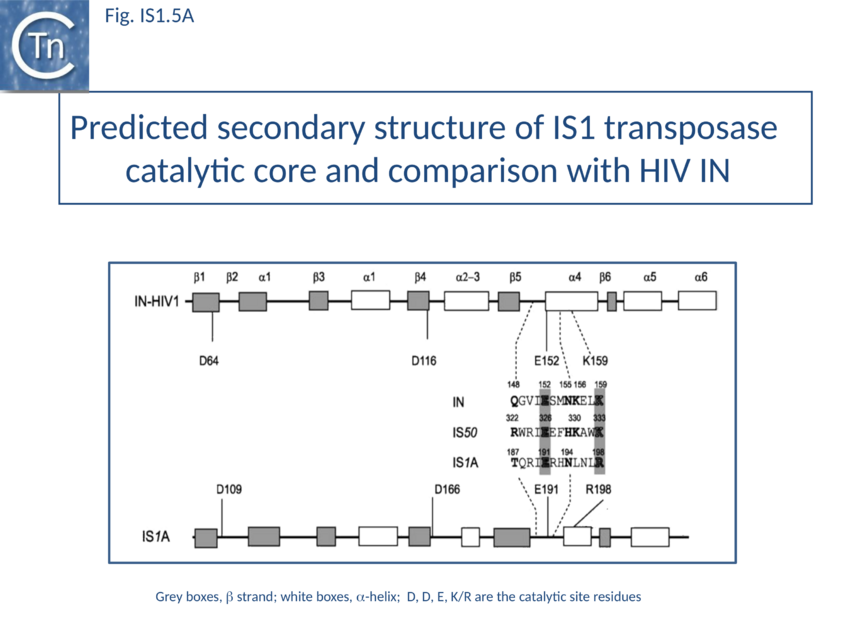
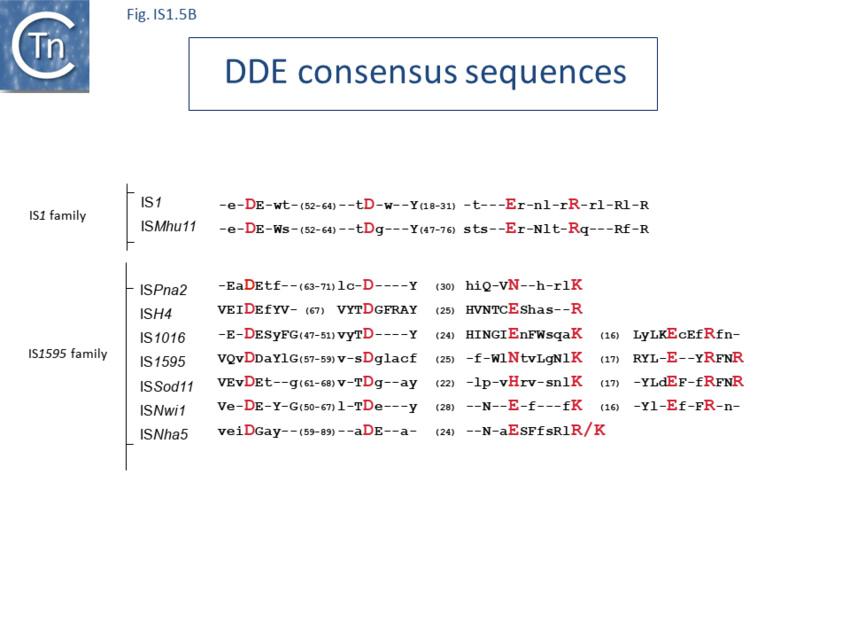
The IS1 family can be divided into two subgroups, IS1 and ISMlu11. This is clearly apparent from the results of MCL clustering (Fig. 1.5.1) which also shows the IS1 family is closely related to another family, IS1595 (IS1595 family). This division is also clear from a consideration of the consensus sequences of the DDE catalytic site (Fig. IS1.5B).
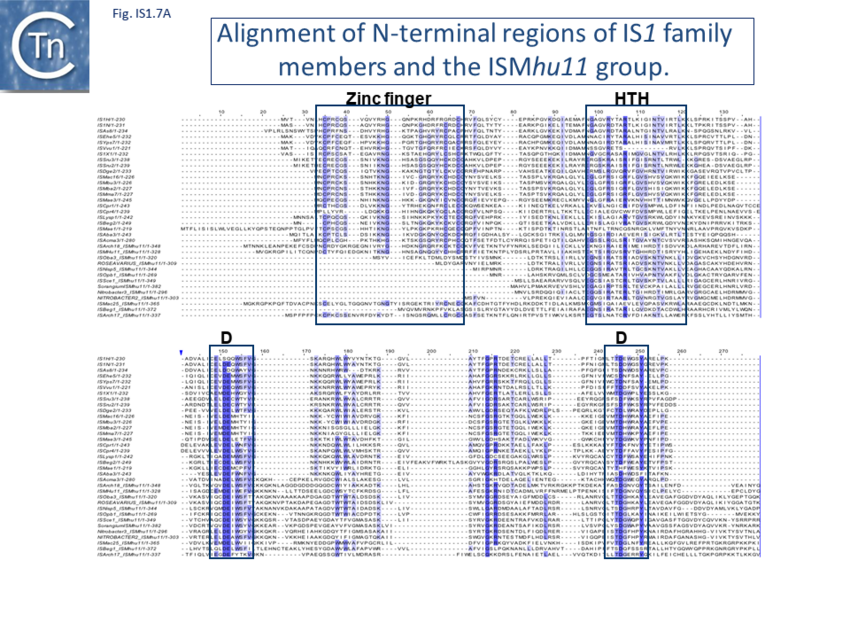
Alignment of the transposase, InsAB’, from different family members confirmed the presence of a C-terminal DDE catalytic domain[43] and also revealed potential N-terminal zinc finger (ZF) and helix-turn-helix (HTH) motifs[44][45] (Fig. IS1.6, IS1.7A). That this ZF plays a functional role is evidenced by the observation that addition of 1,10-phenanthroline, which shows a high affinity for zinc, prevented binding of a transposase derivative to IS1 IR as did mutations in either the ZF or HTH motifs whereas mutation of the DDE motif confirmed its importance in catalysis but not in binding[46][47]. All three motifs are also observed in the Tpases with a single long reading frame.
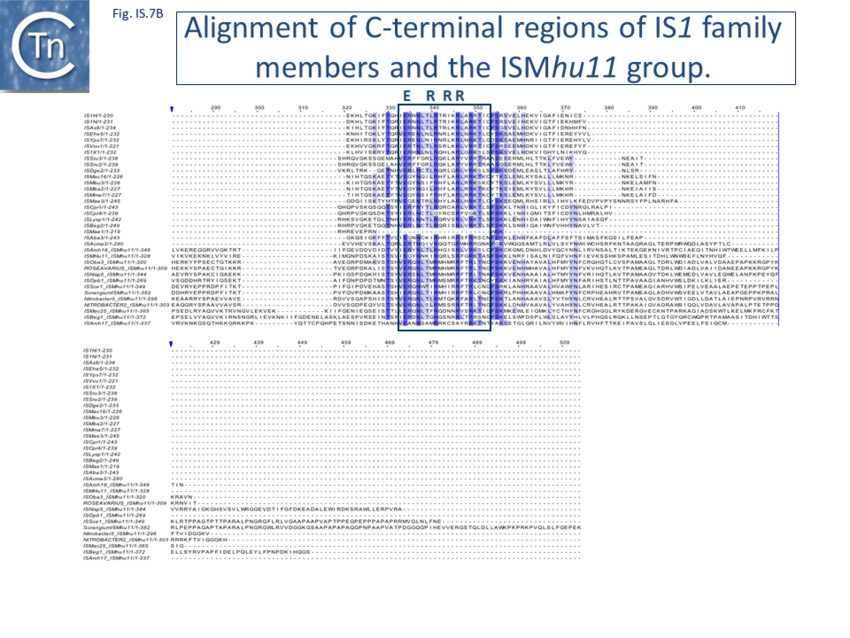
Members of the ISMhu11 subgroup lack the N-terminal ZF while retaining the HTH motif[48] (Fig. IS1.7A and IS1.7B). They also include a 30-120 residue C-terminal extension which is unrelated in different members of this group and the spacing between the second D and E residues is 40-60 amino acids longer. Three different organizations of ISMhu11 subgroup members were identified: examples with two orfs and a potential frameshift zone (ISMhu11, ISMac25, ISArch18 and ISAcma3); a single example with additional non-coding DNA upstream of the Tpase orf (ISBeg1); and members which carry passenger genes (TABLE Characteristics of IS families; Table IS1.1 and Table IS1.2) generally with no known function, but often with other relatives in different bacteria. An exception is tISSce1 (tIS - IS and relatives with passenger genes) which includes orfs resembling a DNA methyltransferase, a possible sigma factor, and member of the HTH_XRE family of transcription regulators. However, only a single example of each type with passenger genes was identified, suggesting that these IS have low or no transposition activity. More extensive comparisons have indicated that IS1 is distantly related to another relatively newly recognized family, IS1595.
| Table IS1.2: Features of derivatives including non-coding DNA or passenger genes. The table summarises from left to right: the IS name; family; group; accession number; host organism; overall length; terminal IR length; number of base pairs duplicated on insertion (DR); the type and order of passenger genes carried (hyp, hypothetical protein; tpa, transposase; tre, transcriptional regulator; met, DNA methyltransferases; pol, RNA polymerase sigma factor; lin, O-lincosamide nucleotidyltransferase; dih, dihydrofolate reductase; pha, Phage related protein; duf955, protein of unknown function DUF955; rel, RelE-like cytotoxic translational repressor of toxin-antitoxin; seg, Chromosome segregation ATPases; kil, KilA domain protein.) | ||||||||
| IS Name | Family | Group | Accession number | Host | L (bp) | IR (bp) | DR (bp) | Content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tISNisp5 | IS1 | ISMhu11 | NZ_AAMY01000028 | Nitrobacter sp. Nb-311A | 3580 | 18 | 8 | hyp, tpa |
| tISOba3 | NZ_AAMO01000002 | Oceanicola batsensis HTCC2597 | 2598 | 26/28 | 8 | hyp, hyp, tpa, hyp | ||
| tISOpb1 | ABEA01000009 | Opitutaceae bacterium TAV2 | 4054 | 65/67 | 8 | hyp, tpa, hyp, hyp, hyp | ||
| tISSce1 | NC_010162 | Sorangium cellulosum 'So ce 56' | 4601 | 17 | 8 | tpa, met, pol, tre | ||
| tISBwe1 | IS1595 | ISPna2 | NC_010180 | Bacillus weihenstephanensis pBWB401 | 1536 | 22/26 | 0 | tpa, hyp |
| tISSag10 | AY928180 | Streptococcus agalactiae | 1724 | 22/25 | 8 | tpa, lin | ||
| tISBsp1 | ABCF01000016 | Bacillus sp. | 1665 | 25/28 | 8 | tpa, hyp | ||
| tISCac2 | NC_003030 | Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC824 | 1838 | 21/25 | 9 | tpa, dih | ||
| tISCba1 | NZ_ABEZ02000022 | Clostridium bartlettii | 2623 | 25/28 | 8 | tpa, hyp, hyp | ||
| tISClph1 | NC_010001 | Clostridium phytofermentans | 1607 | 22/24 | 8 | tpa, hyp | ||
| tISNwi2 | ISNwi1 | NC_007406 | Nitrobacter winogradskyi | 1750 | 21/23 | 5 | tpa, hyp | |
| tISRhba1 | NZ_AAMT01000005 | Rhodobacterales bacterium | 2457 | 23/27 | 8 | tpa, pha | ||
| tISRpa1 | NC_007778 | Rhodopseudomonas palustris HaA2 | 2091 | 27/28 | 8 | tpa, hyp | ||
| tISMesp1 | NC_008254 | Mesorhizobium sp. BNC1 | 2601 | 30/33 | 8 | tpa, duf955 | ||
| tISNwi3 | NC_007406 | Nitrobacter winogradskyi | 2345 | 22/24 | 8 | tpa, pha | ||
| tISNisp2 | NZ_AAMY01000002 | Nitrobacter sp. Nb-311A | 2637 | 20/24 | 8 | tpa, pha, hyp, hyp, hyp | ||
| tISApr4 | NZ_ABHC01000005 | Alpha proteobacterium BAL199 | 3691 | 20/25 | 8 | tpa, hyp, hyp, duf955, hyp | ||
| tISBun1 | NZ_AAYH02000038 | Bacteroides uniformis ATCC 8492 | 2700 | 28/30 | 8 | hyp, tpa, hyp, hyp, hyp | ||
| tISMpo2 | NZ_ABFR01000015 | Methylobacterium populi | 3089 | 27/33 | 8 | tpa, hyp, hyp | ||
| tISBvu2 | NC_009614 | Bacteroides vulgatus ATCC 8482 | 4641 | 22/23 | 8 | tpa, hyp, hyp, hyp,/i>, hyp | ||
| tISBun2 | NZ_AAYH02000036 | Bacteroides uniformis ATCC 8492 | 4739 | 25/27 | 8 | tpa, hyp, hyp, hyp, hyp | ||
| tISVer1 | NZ_ABOX01000007 | Bacterium Ellin514 | 2783 | 22/25 | 8 | tpa, hyp, hyp, hyp, hyp | ||
| tISApr7 | NZ_ABHC01000017 | Alpha proteobacterium BAL199 | 3923 | 25/30 | 8 | tpa, met, hyp | ||
| tISNwi4 | ISNha5 | NC_007406 | Nitrobacter winogradskyi | 3671 | 23 | 8 | hyp, tre, tpa, hyp | |
| tISNha5 | CP000319 | Nitrobacter hamburgensis X14 | 3904 | 27 | 8 | hyp, tre, tpa, hyp, hyp | ||
| tISRpa4 | NC_007925 | Rhodopseudomas palustris BisBl8 | 4218 | 25/26 | 8 | hyp, hyp, tre, tpa | ||
| tISAzca1 | NC_009937 | Azorhizobium caulinodans | 4520 | 24/25 | 8 | tre, tpa | ||
| tISAusp1 | NZ_AAPJ01000002 | Aurantimonas sp. SI85-9A1 | 3418 | 25/28 | 8 | hyp, tre, tpa, rel, hyp | ||
| tISRssp2 | NZ_AAMV01000009 | Roseovarius sp. 217 | 4633 | 26 | 8 | hyp, tre, tpa, hyp, hyp, hyp | ||
| tISSst2 | NZ_AAYA01000001 | Sagittula stellata E-37 | 3454 | 35 | 8 | tre, tpa, seg, seg | ||
| tISRosp3 | NZ_AAYB01000002 | Roseobacter sp. CCS2 | 3472 | 25 | 8 | hyp, tre, tpa, kil, hyp | ||
| tISDsh3 | NC_009952 | Dinoroseobacter shibae DFL 12 | 3472 | 26/27 | 8 | hyp, duf955, tre, tpa, hyp, hyp | ||
| tISCausp2 | NC_010338 | Caulobacter sp. | 7916 | 25/27 | 8 | hyp, hyp, hyp, hyp, tre, hyp, tpa, hyp, hyp, hyp | ||
Non-canonical IS1 derivatives in bacteria and archaea
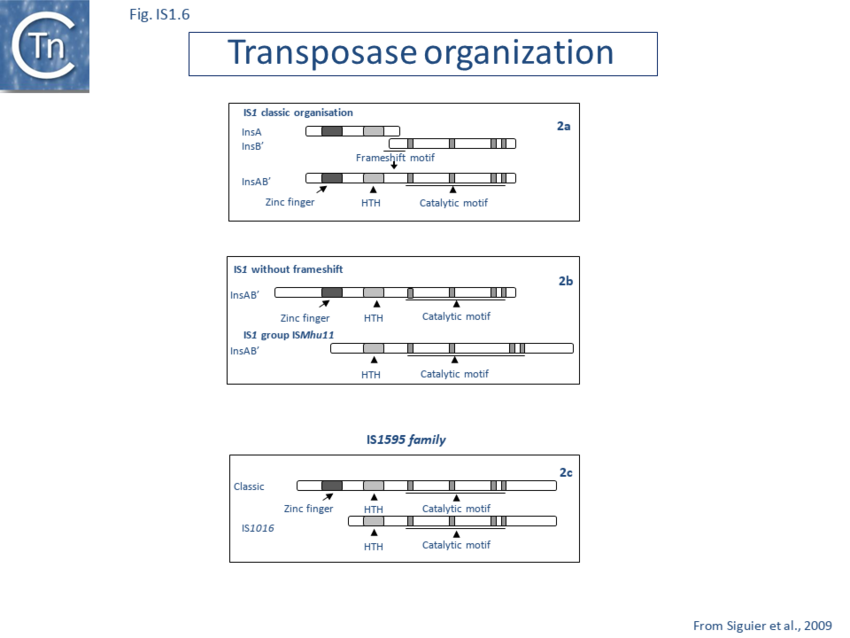
IS1-related derivatives carrying only a single orf have been identified (Fig. IS1.6). These include bacterial members such as ISAba3 (Acinetobacter baumani)[49] and possibly ISPa14 (Pseudomonas aeruginosa) but these derivatives have yet to be demonstrated to transpose[50]. They tend to be longer (~1000 bp) than the classic IS1 with slightly longer Tpases due to an N-terminal extension (TABLE Characteristics of IS families; Table IS1.1). They retain the characteristic IS1 IR sequences (Table IS1.1). This type of IS1 has been identified in the archaeal Sulfolobiales (ISC1773a and b and ISSto7) where the arrangement appears to be the rule[51]. The IS1 members identified in different Sulfolobus species, ISC1173a (S. solfataricus) and ISSto7 (S. tokodaii), are closely related as are ISC796 (Sulfolobus sp.) and ISSto9 (S. tokodaii). Under our operational nomenclature, however, neither ISC1173a and ISSto7 nor ISSto9 and ISC796 are iso-forms. Nevertheless the two pairs are phylogenetically closely related (91% and 84% amino acid identity respectively).
S. tokodaii carries both full length and solo ISSto7 IRs together with 2 complete small ISSto7-derived MITE-like elements (see Non-autonomous IS derivatives) with sizes of 315 and 317 bp. ISC796 is present as a single copy in Sulfolobus sp. and as several fragmented copies in S. solfataricus. There are both complete and partial copies of ISSto9 in S. tokodaii, and solo IRs. ISC1173a and ISSto7 are significantly longer (1173 and 1174 bp) than other family members with IRs of approximately 50 bp, over twice the length of other members of the family. Moreover the Tpase is larger than that of ISC796, ISSto9 and other members of the family (~340 compared to ~240) due to an 80 amino acid N-terminal extension and a 40 amino acid C-terminal extension. Both ISC796 and ISSto9 are 796 bp long with IRs of 21 bp. DNA alignments show that the long and short ISs and the MITES are clearly derived from a common ancestor but their exact relationship is at present unclear.
Although there is no orf equivalent to insA, in principle, an upstream equivalent to InsA might be produced in these single orf elements. This could occur, for example, by post translational proteolysis of the larger transposase or by frame-shifting to create the smaller protein, as in dnaX of Escherichia coli[52] or by transcription termination within the IS.
Canonical archaeal IS1 derivatives
Certain archaeal IS1 family members are organised in the same way as are canonical eubacterial IS1. These are present in the Methanosarcinales: ISMac16 (Methanosarcina acetivorans); ISMma7 (M. mazei, M. barkeri and Methanococcoides burtonii), ISMba2 (M. barkeri) and ISMbu3 (Methanococcoides burtonii). ISMac16, ISMma7 and ISMba2 are 740 bp long with 24 bp IRs and 8 or 9 bp DRs. ISMbu3 (741 bp; 8 bp DRs) has IRs of only 15 bp. In contrast to the Sulfolobus IS1 members, these all carry the expected two orfs. They are closely related elements with 84-89% identity with respect to ISMac16. Inspection of their nucleic acid sequence reveals an appropriately placed stretch of 8 A residues and raises the possibility that the transposase is produced by transcriptional rather than translational frameshifting[53].
The transposases of these elements are related to that of ISMae3 of the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa[54] and less closely to diverse IS1 elements of -Proteobacteria including IS1X and IS1S from E. coli and ISVvu1 from Vibrio vulnificus. The DDE catalytic motif and surrounding amino acid residues are also typical of this family. Finally, the terminal 23 to 30bp are very similar to the IRs of the -Proteobacterial and cyanobacterial IS1 elements and terminate with a highly conserved 5’ GGNNNTG (CANNNCC3’). Where identified, the site of insertion is A+T rich.
Target specificity
Insertion of IS1 shows little sequence-specificity but occurs within relatively AT-rich regions of the target DNA[55][56][57].
Transposase expression by programmed translational frameshifting
Classical IS1family members also carry two partly overlapping open reading frames (insA and insB’) located in the 0 and -1 relative translational phases[58][59] and expressed from a promoter, pIRL, partially located in IRL[60] (Fig. IS1.1). Their integrity is essential for transposition. The Tpase is produced by programmed -1 ribosomal frameshifting (PRF) between insA and insB’ with typical frameshift signals (a set of slippery codons; Fig. IS1.1), an upstream ribosome binding site and downstream secondary structures (see [61]). PRF occurs at a frequency of about 1%. The site of frameshifting is an A6C motif located at the 3’ end of the upstream insA frame[62][63][64][65] (Fig.1.33.1).
Natural transposition of IS1 occurs at a relatively low frequency (approximately 10-7 in a standard mating assay). Insertion of an additional A residue within the A6C motif to yield A7C or replacement of the motif with GA2GA3C fuses the two reading frames, leading to constitutive production of the Tpase while eliminating the production of InsA (see Fig. IS1.6). This results in levels of transposition of between 0.1 and 1% in vivo in a standard mating out[66] assay[67][68][69][70][71][72]. No significant levels of InsB’ could be detected. Frameshifting fuses the product of the upstream insA frame with that of the downstream insB’ frame to generate the Tpase as a fusion protein, InsAB’, which includes a C-terminal catalytic DDE motif and N-terminal zinc finger and helix-turn-helix motifs[73][74][75] important for transposase binding.
The small, more abundant basic InsA protein binds specifically to the IRs[76][77][78] and acts as a repressor of the Tpase promoter, pIRL, partly included in the left end[79][80] (Fig. IS1.1). It also appears to inhibit transposition directly, probably by competing with the InsAB’ Tpase for binding to the ends of the element[81]. Overall transposition activity appears to depend on the ratio of InsA/InsAB’, serving to regulate activation of transposition by uncontrolled Tpase expression from external transcription[82]. Since this ratio is set by the frequency of frameshifting and is relatively insensitive to the intensity of transcription, the arrangement ensures that IS1 is not activated by high levels of impinging transcription following insertion into highly expressed genes.
It had been suggested that a translational restart within the insA frame giving rise to an InsAB’ protein with an N-terminal deletion generates the true Tpase[83] . However, while the importance of this protein cannot be ruled out, the establishment of an in vitro IS1 transposition system based on partially purified engineered InsAB’ suggests that the translational restart product may not play a central role[84].
Interestingly, InsAB’ was found to copurify with GroEL[85]. It remains to be determined whether GroEL plays a role in the normal transposition process as a cofactor or whether overproduction of InsAB’ and potential misfolding of the protein is the trigger for InsAB’/GroEL interactions.
Transcription termination?
An additional control of Tpase expression may be exercised at the level of transcription termination. Early studies on IS1 organization identified a region at the end of the insA gene which behaves as a Rho-dependent transcription terminator[86]. Premature transcription termination would therefore result in the production of an mRNA lacking the insB’ frame. The role of this sequence in the control of IS1 transposition remains to be determined.
Moreover, the transposase termination codon is often located within the distal IR which may reflect an, as yet unknown regulatory function.
Mechanism
IS1 generates both simple insertions and replicon fusions (cointegrates) composed of two directly repeated copies of the IS, one at each junction between the target and donor replicons. Such structures are relatively stable and constitute a pathway for formation of new compound transposons. The occurrence of stable cointegrates as transposition end products led to the suggestion that transposition of IS1 can proceed in a replicative manner[87] while simple insertions may occur without replication[88]. Thus, IS1 may be capable of both replicative and conservative transposition. More convincing evidence in support of a duplicative transposition pathway was obtained by analysing the products of intramolecular transposition[89]. In vivo, direct visualization of 13 DNA species obtained following induction of IS1 transposition and the kinetics of their appearance and disappearance clearly identified forms corresponding to the reciprocal products of IS-mediated deletions, as well as excised transposon circles. This suggests that IS1 can transpose using both the cointegrate (target primed replicative transposition) and copy-out paste-in (donor primed transposon replication) pathways[90].
High levels of InsAB' in the presence of suitable IS1 ends induce the host SOS response, possibly reflecting endonucleolytic activity of the IS1 Tpase[91]. By using this in vivo assay system, originally developed for screening mutants of the IS10 Tpase (see " IS4 family"), it was possible to show that for relatively short artificial derivatives of IS1, the level of response depends in a periodic manner on the distance between the ends. The periodicity was found to be about 10 to 11 bp and was also reflected in the transposition activity, suggesting a requirement for correct helical positioning of both ends. Two directly repeated ends were also capable of eliciting the SOS response, although they were not capable of giving productive transposition. In addition, these and other studies[92]9218718 detected excised circular copies of the IS1-derived transposon, and it was suggested that, as in the case of IS911 (see "IS3 family"), such forms may integrate into a target molecule to give rise to simple insertions. A related type of transposition mechanism was previously proposed for IS1 transposition. More recent experiments confirmed that such circles in which the IS ends are separated by a spacer of 6-9 bp are active in transposition and integrate with high efficiency. Insertion generates a typical target DR and is accompanied by loss of the spacer sequence Shiga[93].
A cell-free in vitro transposition system has been described using partially purified InsAB’[94]. In this assay, an IS1 circle junction carrying abutted IRR and IRL copies was shown to integrate into a covalently closed circular plasmid to produce one- and two-ended transposition events. It was also shown that if one IR in the junction was mutated at its tip such that it was no longer functional on its own, it could be rescued by the second, wildtype, copy in the donor IRL-IRR junction. This reaction was dependent on Mg2+ ions and the presence of the InsAB’ protein together with its accompanying groE chaperone (removal of the chaperone eliminated transposition activity).
Bibliography
- ↑ <pubmed>4567156</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>4567154</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>375010</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>273224</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>1849492></pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>1061090</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>368646</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>6254008</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>5327907</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>14234780</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>6281439</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>385225</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>2999083</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>4278060</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>4942895</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>4911539</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>323231</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>385225</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>7003302</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>6285398</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>895711</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>385224</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>6306398</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>6265806</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>6258088</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>8905231</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>10673006</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>350411</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>350412</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>6328213</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>2983315</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>3038535</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>3038535</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>6086942</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>2851480</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>6086943</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>2995832</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>3302598</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>1962838</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>6281761</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>6313938</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>6309405</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>12399484</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>15225314</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>15387827</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>15225314</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>15387827</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>19286454</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>15616297</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>19286454</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>17347521</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>2186364</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>16460832</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>15387827</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>6260963</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>6248730</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>2997452</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>6086942</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>2851480</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>6086943</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>24875478</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>1848178</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>2543983</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>1334530</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>1334529</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>6281440</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>1848178</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>2543983</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>1334530</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>1334529</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>6281440</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>8083181</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>12399484</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>15225314</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>15387827</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>1962838</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>2826132</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>2162466</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>2162466</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>2553980</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>1848178</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>1848178</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>8021940</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>15387827</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>15387827</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>3029382</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>6281440</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>6094304</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>7489730</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>7489730</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>7932694</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed></pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>10583504</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>15387827</pubmed>