Difference between revisions of "General Information/Overview"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{| | {| | ||
| − | |- | + | |-vertical-align:super; |
| − | + | | | |
'''<big>T</big>'''he idea that many prokaryotic genomes are mosaic, composed of a "central genome backbone" of essential and house-keeping genes (the core genome) interspersed with DNA segments constituting the "mobilome" (a variety of accessory genes that form part of the pan-genome)[[:Image:fig1.png|(Fig.1.1.1)]], is now common currency <ref name=":0"><pubmed>16185861</pubmed></nowiki></ref><ref name=":1"><pubmed>19086349</pubmed></nowiki></ref>. | '''<big>T</big>'''he idea that many prokaryotic genomes are mosaic, composed of a "central genome backbone" of essential and house-keeping genes (the core genome) interspersed with DNA segments constituting the "mobilome" (a variety of accessory genes that form part of the pan-genome)[[:Image:fig1.png|(Fig.1.1.1)]], is now common currency <ref name=":0"><pubmed>16185861</pubmed></nowiki></ref><ref name=":1"><pubmed>19086349</pubmed></nowiki></ref>. | ||
The mobilome embraces several types of genetic units which, as their collective name indicates, can move from place to place in a particular genome or from cell to cell. These [[wikipedia:Mobile_genetic_elements|mobile genetic elements]] (MGE) can be divided into two major groups: those, such as plasmids and bacteriophages, that are transmissible from cell to cell (the intercellular MGE), and those that cannot themselves undergo transfer but which are transferred following integration into members of the first group (the intracellular MGE). | The mobilome embraces several types of genetic units which, as their collective name indicates, can move from place to place in a particular genome or from cell to cell. These [[wikipedia:Mobile_genetic_elements|mobile genetic elements]] (MGE) can be divided into two major groups: those, such as plasmids and bacteriophages, that are transmissible from cell to cell (the intercellular MGE), and those that cannot themselves undergo transfer but which are transferred following integration into members of the first group (the intracellular MGE). | ||
Revision as of 14:12, 7 May 2020
|
The idea that many prokaryotic genomes are mosaic, composed of a "central genome backbone" of essential and house-keeping genes (the core genome) interspersed with DNA segments constituting the "mobilome" (a variety of accessory genes that form part of the pan-genome)(Fig.1.1.1), is now common currency [1][2]. The mobilome embraces several types of genetic units which, as their collective name indicates, can move from place to place in a particular genome or from cell to cell. These mobile genetic elements (MGE) can be divided into two major groups: those, such as plasmids and bacteriophages, that are transmissible from cell to cell (the intercellular MGE), and those that cannot themselves undergo transfer but which are transferred following integration into members of the first group (the intracellular MGE). Intracellular MGE or transposable elements (TE) include transposons (Tn) and insertion sequences (IS) but can embrace integrons (In) [3][4] and introns [5][6][7]. Originally Tn were distinguished from IS since they carry passenger (also called cargo) genes not involved in catalyzing or regulating TE movement. Most eukaryotic DNA transposons have relatives among the prokaryotic IS (see [8]) and it is not surprising that a variety of these elements carrying passenger genes are now also being identified [9][10]. Prokaryotes harbor a host of such elements as well as several types of structure possessing characteristics of both groups (e.g. Integrative Conjugative Elements, ICE, originally called conjugative transposons, as well as other types of non-conjunctive genomic islands) [11][12][13].
|
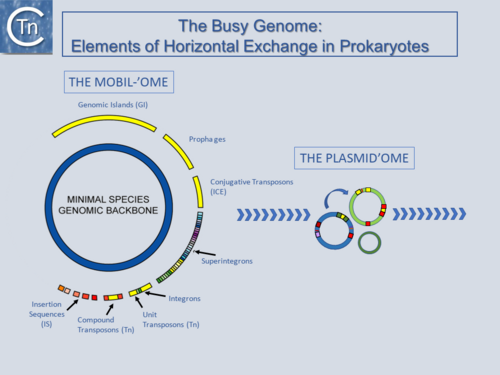 Fig.1.1.1. The Busy Genome: Elements of Horizontal Exchange. The genome backbone, which includes housekeeping genes, is shown as the inner circle (blue). The "mobilome" is shown in the outer circle. This includes a number of different types of MGE both intercellular (some genomic islands, prophages, and conjugative transposons) and intracellular (Insertion sequences, compound and unit transposons, integrons, and super integrons). An important class of intercellular MGE, the plasmids, act as transposon vectors and facilitate TE movement within the plasmidome. |
Bibliography
- ↑ <pubmed>16185861</pubmed></nowiki>
- ↑ <pubmed>19086349</pubmed></nowiki>
- ↑ <pubmed>26104695</pubmed></nowiki>
- ↑ <pubmed>26961432</pubmed></nowiki>
- ↑ <pubmed>26104554</pubmed></nowiki>
- ↑ <pubmed>25960782</pubmed></nowiki>
- ↑ <pubmed>26104699</pubmed></nowiki>
- ↑ <pubmed>20067338</pubmed></nowiki>
- ↑ <pubmed>19174482</pubmed></nowiki>
- ↑ <pubmed>23548000</pubmed></nowiki>
- ↑ <pubmed>15207870</pubmed></nowiki>
- ↑ <pubmed>15100694</pubmed></nowiki>
- ↑ <pubmed>23435978</pubmed></nowiki>